Urban Poverty In Malaysia 2019

In 2014 the poverty threshold was rm930 in peninsular malaysia rm990 in sarawak and rm1 170 in sabah and labuan.
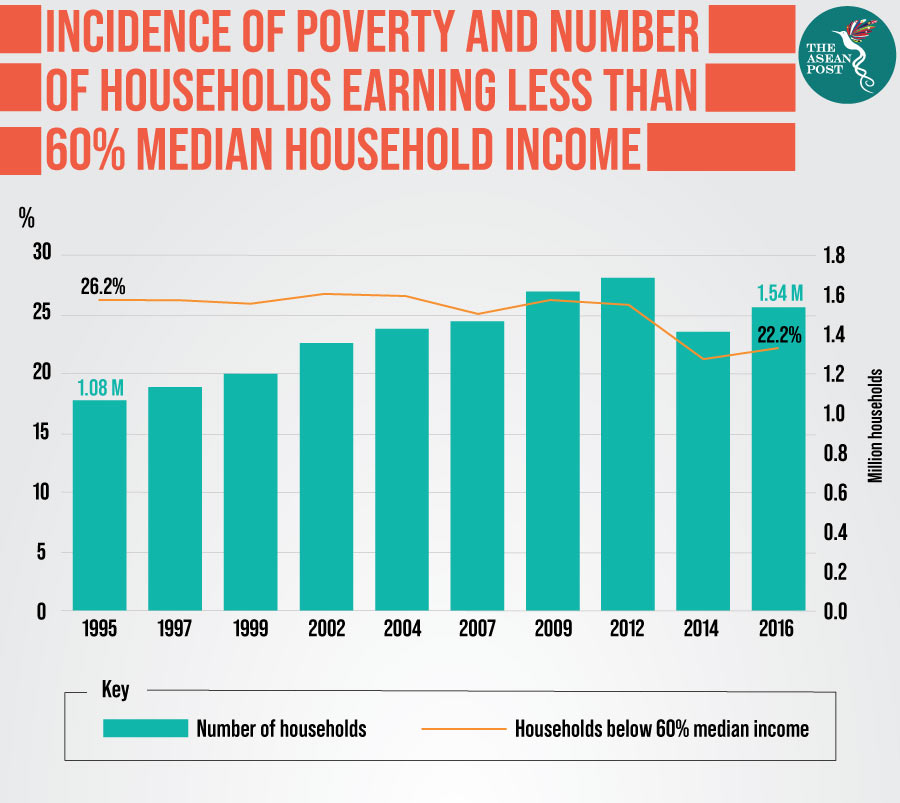
Urban poverty in malaysia 2019. Urban poverty is inextricably linked to rural poverty. 33 while urban relative poverty in 2019 came in at 12 8 against 11 1 in 2016. In fact the former is caused by the latter. Picture by shafwan zaidon.
Malaysia has raised its poverty line by more than 100. Reports that urban poverty in malaysia is not considered a serious phenomenon. Reviews past and present trends of urbanization and urban poverty especially in the metropolitan city. Reduction in the incidence of poverty has reduced in both urban and rural areas.
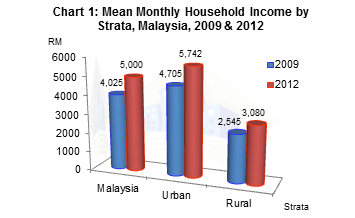
However rapid urbanization and industrialization is expected to bring in rural migrants into urban centres bringing along low incomes while putting pressure on urban services infrastructure and the environment. Malaysia s official poverty rate dropped from 49 per cent in 1970 to just 0 4 per cent in 2016. However the national poverty line of rm 980 us 235 per household per month would see an urban family of four surviving on rm 8 or less than us 2 per person per day. While the goal of faster development manifest through commercialization modernization and urbanization contributed to urban biased development strategy the lack of.
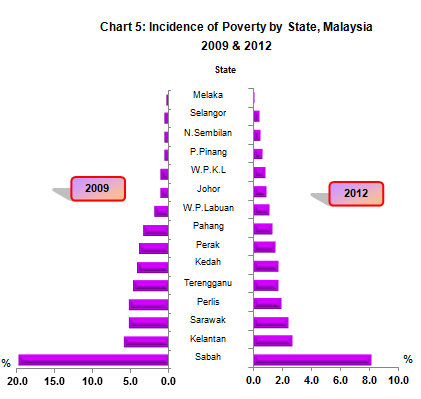
Prof jayasooria who is with universiti kebangsaan malaysia has researched urban poverty over 25 years. Incidence of poverty in all states have declined with the most significant improvement was sabah from 4 0 per cent in 2014 to 2 9 per cent in 2016. Similarly poverty incidence in the urban and rural areas depicted the same trend whereby it decreased to 0 2 per cent and 1 0 per cent respectively. September 2 2019 7 00 am.
Kuala lumpur june 25 the number of poor malaysians is higher than official figures if the relative poverty line reflects today s reality khazanah research institute kri said. Time for higher minimum wage. The real urban poor are those with odd jobs. If the 2005.
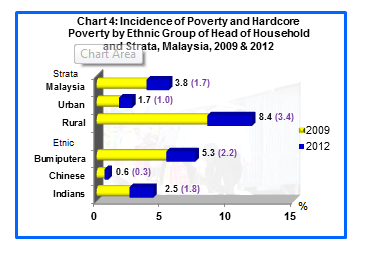
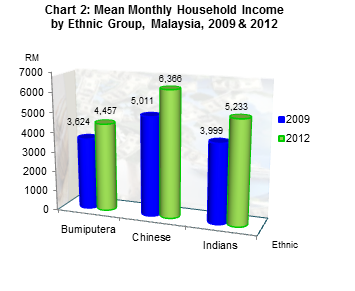
The incidence of poverty in malaysia decreased substantially from 3 8 in 2009 to 1 7 in 2012. 2016 revealed that there is a downward trend in urban poverty in peninsular malaysia indicated by the poverty rate in urban areas decreasing from 25 5 percent in 1970 to one. The pull and the push factors can significantly explain the prevailing dismal conditions associated with urban poverty.